Polycarbonate (PC) sheets are widely used in construction, agriculture, transportation, and other fields due to their excellent properties such as good light transmission, high impact resistance, and strong weather resistance. The following is a detailed introduction to the differences and applications of polycarbonate roof sheets, solid polycarbonate sheets, and twin wall polycarbonate sheets in terms of structure, performance, distinctions, and application scenarios:
I. Basic Structure and Performance Characteristics of Products
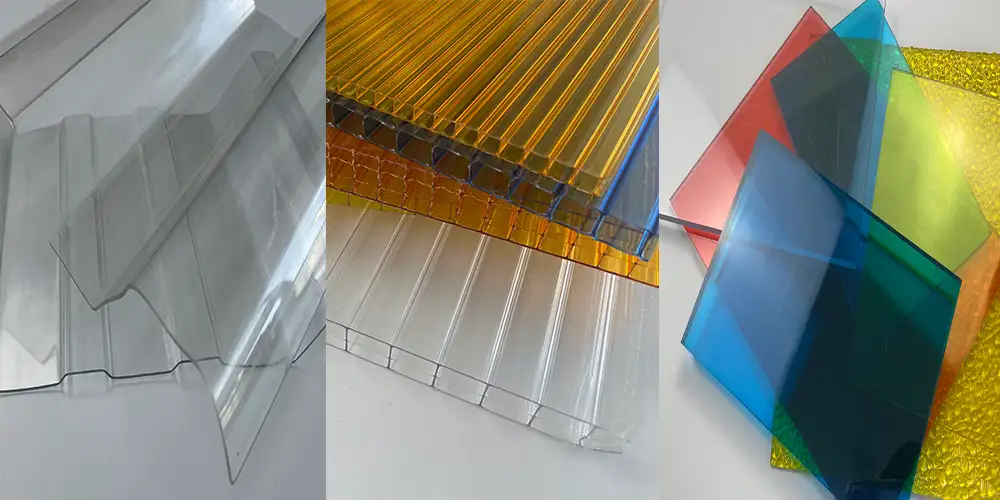
1. Polycarbonate Roof Tiles
- Structure: Usually single-layer sheets with a corrugated or trapezoidal shape, thin in thickness (generally 1-3mm), and the surface may be coated with an anti-ultraviolet layer.
- Performance:
- Lightweight, easy to install, suitable for large-span roof covering;
- Moderate light transmittance (about 50%-70%), meeting basic lighting needs;
- Better impact resistance than traditional tiles (such as asbestos tiles and cement tiles), but weaker than solid and multi-layer PC sheets;
- General heat insulation performance, requiring matching with insulation layers.
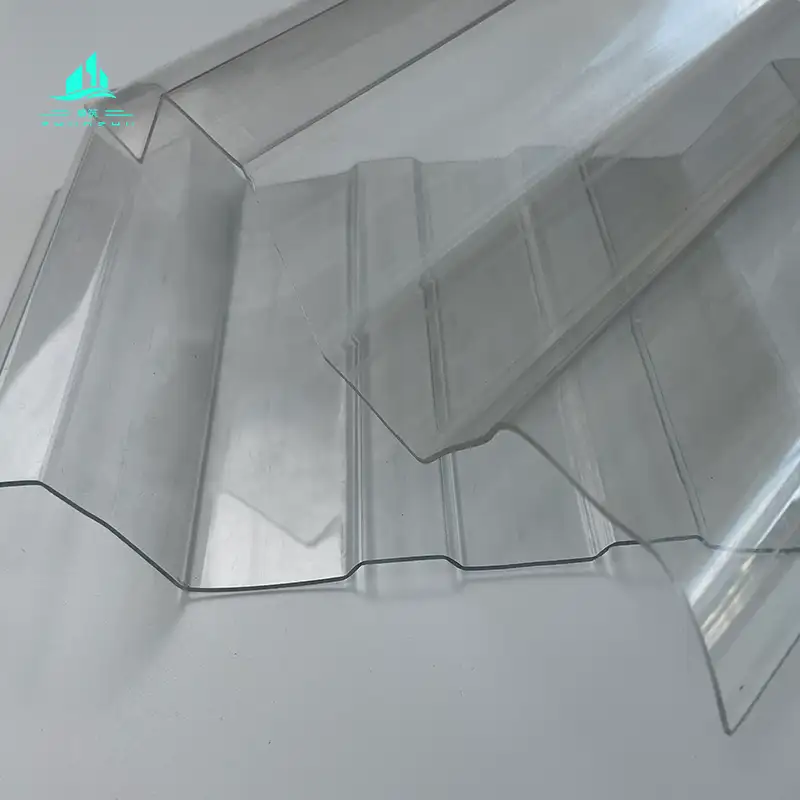

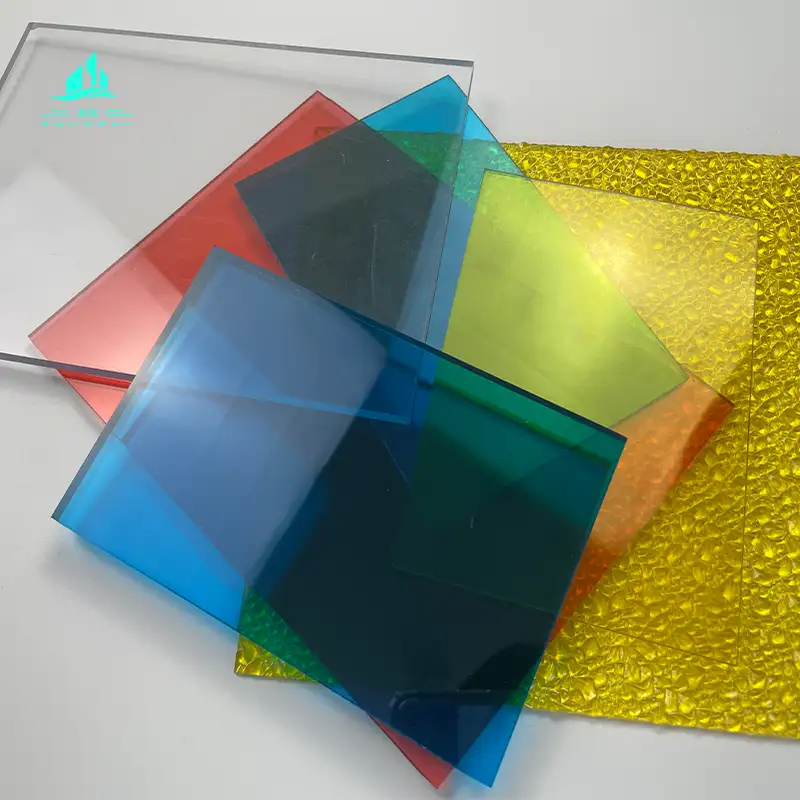
2. Solid Polycarbonate Sheets
- Structure: Solid sheets without a hollow structure, with a wide thickness range (2-20mm or even thicker), and hard texture.
- Performance:
- High light transmittance (up to 80%-90%), close to glass, and the light is soft and not dazzling;
- Extremely strong impact resistance (250-300 times that of ordinary glass), with high safety;
- Good weather resistance, able to resist ultraviolet rays, high and low temperatures (-40℃ to +120℃), and wind and rain erosion;
- Weight is only 1/2 of that of glass, convenient for transportation and installation, but heat insulation performance is weaker than that of multi-layer sheets.
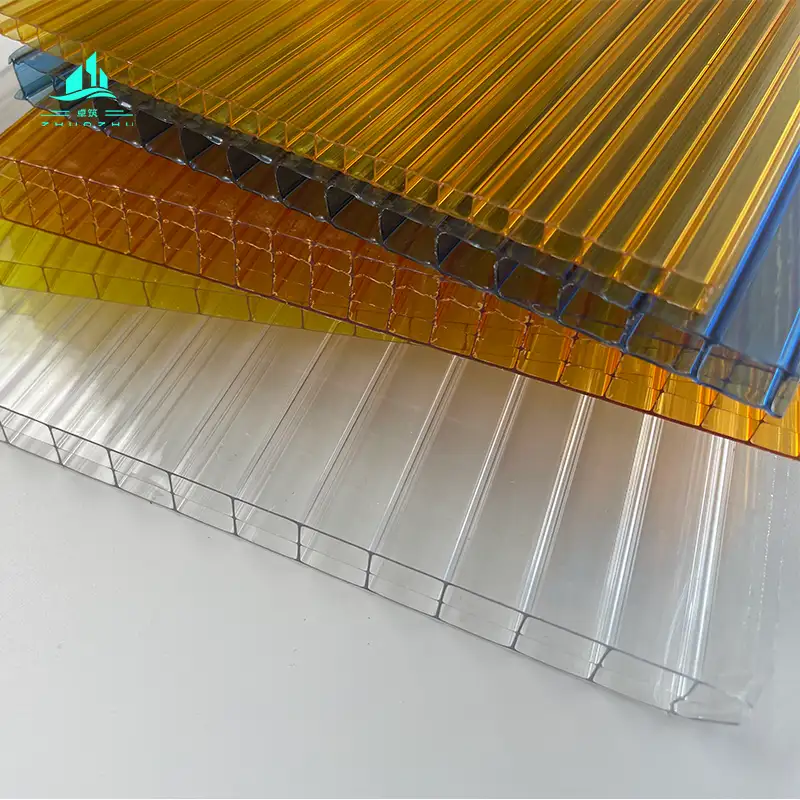
3. Multi-layer Polycarbonate Sheets (also known as hollow PC sheets)
- Structure: Formed by connecting multiple layers of flat plates through ribs to form a hollow structure (commonly 2-layer, 3-layer, 4-layer, or honeycomb-shaped), with a thickness of 5-40mm.
- Performance:
- Relatively high light transmittance (60%-85%), and glare can be reduced through structural design;
- The hollow structure gives it excellent heat insulation and sound insulation performance (thermal conductivity is only 1/4 of that of glass);
- Strong impact resistance (better than glass and roof tiles), lightweight (lighter than solid PC sheets);
- Weather resistance is equivalent to that of solid sheets, and due to the hollow design, the thermal insulation and energy-saving effects are prominent.
II. Comparison of Core Differences
| Comparison Dimension | Polycarbonate Roof Tiles | Solid Polycarbonate Sheets | Twin Wall Polycarbonate Sheets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single-layer, corrugated/trapezoidal | Solid, non-hollow | Twin wall, hollow (with ribs) |
| Thickness | Thin (1-3mm) | Thick (2-20mm+) | Medium to thick (5-40mm) |
| Light Transmittance | Moderate (50%-70%) | High (80%-90%) | Relatively high (60%-85%) |
| Impact Resistance | Stronger (better than traditional tiles) | Extremely strong (best among PC sheets) | Strong (better than roof tiles, weaker than solid sheets) |
| Heat/Sound Insulation | General | Weak | Excellent (advantage of hollow structure) |
| Weight | Lightest | Heavier (under the same thickness) | Lighter (30%-50% lighter than solid sheets) |
| Cost | Lowest | Highest | Medium (higher than roof tiles, lower than solid sheets) |
III. Application Scenarios
1. Polycarbonate Roof Tiles
- Core Advantages: Cost-effective, lightweight, suitable for large-area covering, replacing traditional tiles.
- Typical Applications:
- Roof covering of industrial plants, warehouses, and logistics centers;
- Agricultural greenhouses (for basic lighting and rain protection), livestock breeding sheds;
- Roofs of temporary buildings, sentry boxes, and sunshades;
- Roof renovation of civil houses in rural areas (replacing asbestos tiles and ceramic tiles).
2. Solid Polycarbonate Sheets
- Core Advantages: High light transmittance, high safety (such as replacing glass), suitable for scenarios requiring high light transmission and strength.
- Typical Applications:
- Building skylights (such as replacing glass curtain walls in shopping malls, gymnasiums, and hotels to avoid the risk of glass breakage);
- Protective facilities (highway sound barriers, machine guards, explosion-proof shields);
- Advertising light boxes and display cabinet panels (good light transmittance and strong weather resistance);
- Observation windows of swimming pools and aquariums (water pressure resistance and anti-breakage).
3. Multi-layer Polycarbonate Sheets
- Core Advantages: Excellent heat and sound insulation, lightweight, balanced comprehensive performance, suitable for scenarios requiring both energy saving and lighting.
- Typical Applications:
- Greenhouses (high-end planting, needing to balance lighting and heat preservation, such as flower and seedling sheds);
- Building lighting curtain walls and patio ceilings (such as atriums in office buildings and schools, reducing air conditioning energy consumption);
- Sound barriers (on both sides of urban expressways and railways, balancing light transmission and noise reduction);
- Sunshades and canopies (such as parking lots and station platforms, which can keep out rain, transmit light, and avoid heat);
- Agricultural photovoltaic greenhouses (combining light transmission and heat preservation, taking into account planting and photovoltaic power generation).
IV. Summary
- Choose polycarbonate roof tiles for low cost and basic roof covering;
- Choose solid polycarbonate sheets when high light transmittance and high safety (such as replacing glass) are required;
- Choose twin wall polycarbonate sheets when emphasizing heat and sound insulation, energy saving, weight reduction, and needing to balance light transmission.
In practical applications, the selection should be comprehensively considered based on the specific scenario’s requirements for light transmittance, load-bearing, heat preservation, budget, etc.



